Chinese scientists set record with daytime laser ranging to Moon satellite 130,000 kilometers away
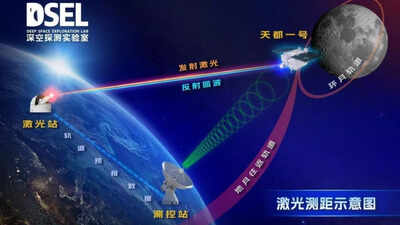
Chinese scientists have marked a significant milestone in space exploration, successfully conducting satellite laser ranging in the Earth-moon space during daylight hours. This achievement overcomes significant daylight interference, paving the way for enhanced deep-space exploration.
Li Yuqiang, a researcher at Yunnan Observatories, announced that his team successfully targeted the Tiandu-1 satellite, located approximately 130,000 kilometers from Earth. The team captured the return signal using a newly upgraded near-infrared lunar laser ranging system integrated with a 1.2-meter telescope. This technological advancement significantly improves navigation and positioning capabilities in the Earth-moon space, providing critical support for future deep-space exploration initiatives.
This groundbreaking experiment, conducted between April 26th and 27th, represents the first successful daytime Earth-to-moon laser-ranging trial. According to xinhuanet.com, China’s Deep Space Exploration Laboratory successfully fired a precision laser from Earth to the Tiandu-1 satellite. Despite intense sunlight interference, the signal was successfully returned.
Researchers at the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences emphasized the significance of this breakthrough in precise deep-space orbit measurement. Previously, this technology was limited to nighttime operations due to sunlight interference. The new achievement boasts centimeter-level accuracy, establishing a new benchmark for future space operations. This advancement is a crucial step forward in support of China's ambitious plan for a crewed lunar mission by 2030.
This accomplishment in laser ranging will dramatically improve the precision of China's lunar missions and further exploration into deep space through accurate orbital measurements and enhanced communications. The success of this experiment also highlights China's advancements in lunar navigation and space communications, enabling more precise and frequent missions to the Moon and beyond.
Also read | Unique rare Earth elements unveiled on an underwater island; here’s what it means for the future
Newer articles
-
 Mahbub Anam replaces Faruque Ahmed as new BPL chairman
Mahbub Anam replaces Faruque Ahmed as new BPL chairman
-
 Suchitra Krishnamoorthi faces backlash for claiming Air India crash survivor was ‘LYING’; Deletes post and issues apology
Suchitra Krishnamoorthi faces backlash for claiming Air India crash survivor was ‘LYING’; Deletes post and issues apology
-
 Pope retains No.3 spot; Carse set for home 'debut'
Pope retains No.3 spot; Carse set for home 'debut'
-
 'Would be remarkable to choose someone else if their last knock was a 170'
'Would be remarkable to choose someone else if their last knock was a 170'
-
 India vs England: Can Bazball outplay India's new era? Key battles and what to expect
India vs England: Can Bazball outplay India's new era? Key battles and what to expect
-
 Will Nysa Devgan enter Bollywood like Raveena Tandon's daughter Rasha Thadani? Kajol reveals the truth
Will Nysa Devgan enter Bollywood like Raveena Tandon's daughter Rasha Thadani? Kajol reveals the truth
-
 Ajinkya Rahane opts against Karun Nair in his India XI for first Test; explains why
Ajinkya Rahane opts against Karun Nair in his India XI for first Test; explains why
-
 5 smart tricks to instantly influence anyone (without being pushy), as per psychology
5 smart tricks to instantly influence anyone (without being pushy), as per psychology
-
 Ngarava, Curran and Raza to miss Test series against South Africa
Ngarava, Curran and Raza to miss Test series against South Africa
-
 iQoo Z9 Turbo new leak reveals key specifications: All the details
iQoo Z9 Turbo new leak reveals key specifications: All the details